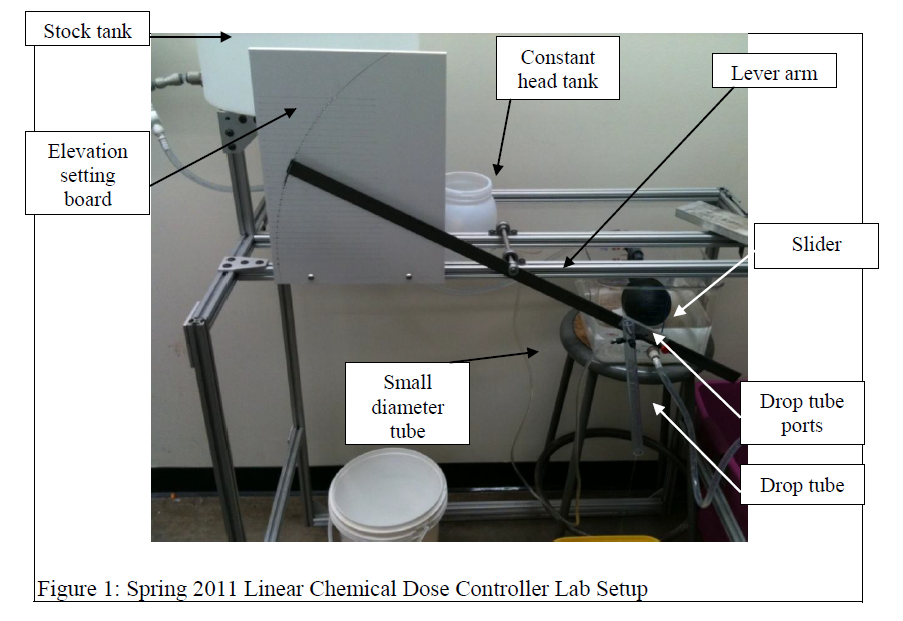
Introduction:
To ease plant preparation for use, it may be beneficial to create stock solutions of required chemicals days in advance of actual operation. Because certain chemical solutions equilibrate with air, they may perform better or worse with age. Using this set of experiments, it was to be determined whether an aluminum sulfate solution produces lower levels of effluent turbidity due to its age.