Jacqueline Dokko, Janak Shah
Abstract
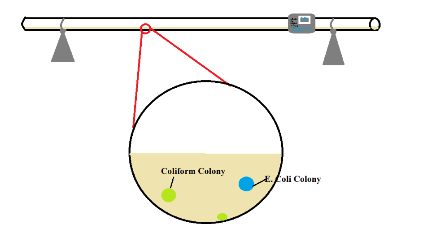
The ultimate goal for the microbiological water safety monitoring (MWSM) team is the development of a test that detects pathogens in water. The test must be of low cost (under ten dollars for each test), have a reduced incubation time from the standard 48 hours, and be able to be used in a low-resource setting such as Honduras. The team tested methods indicating the presence or absence of bacteria compared to quantitatively determining bacterial presence. Upon understanding the cost and efficiency of each method, it was possible to narrow down the methods that could be used as a model for microbial detection for AguaClara purposes.