Theresa Chu, Lucinda Li, Jonathan Harris
Abstract
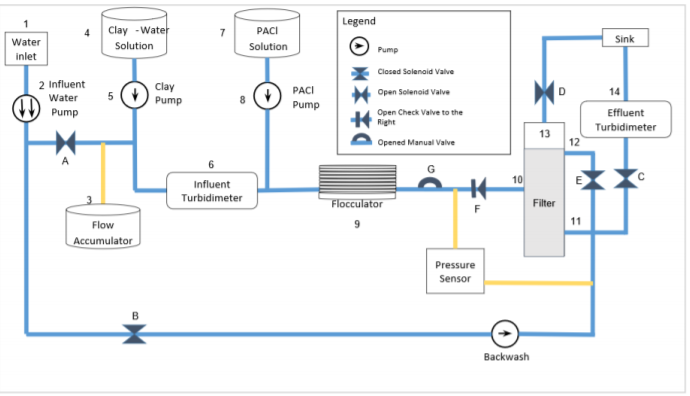
A mathematical model describing sand filtration would promote the understanding of stacked rapid sand filter performance. Variables affecting filter performance include coagulant dosage, influent turbidity, and sand filtration depth. The collected data from a model filter informed a mathematical model explaining the effect of coagulant mass on the filter’s effluent turbidity, head loss, and failure time. Experiment runs demonstrated that increasing coagulant dosage led to an increase in head loss and decrease in time until filter failure as well as vary effluent turbidity. Head loss curves for the various PACl dosages had the same trend after filter failure and converged to the same value after a 24 hour run time.