Abstract:
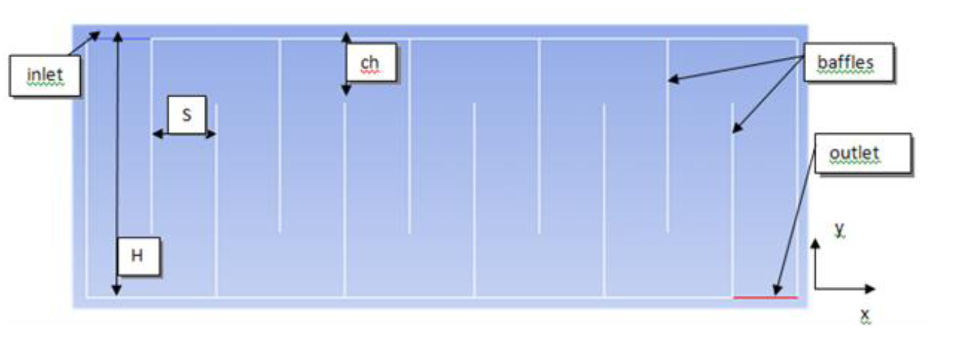
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is a tool used by AguaClara to obtain a description of the flow through a portion of the plant where particle formation and growth (flocculation) occurs. This part of the plant is referred to as the flocculator. In this section, dirty (turbid) water flows through a series of baffles that enhances turbulent mixing. Essentially, for particles (flocs) to grow and eventually settle out in the sedimentation tank, they first must collide. By increasing the level of turbulence, the flocculator is increasing the collision potential of flocs. However, if there is too much turbulence, the flocs will break up and not settle out. By running CFD simulations of the flocculator, AguaClara can analyze the parameters important to flocculation and use the resulting data when making design decisions.